Troubleshooting and Debugging
If you’re having issues with your ICRN environment, try these basic troubleshooting and debugging steps first. If the issue persists, submit a support request and NCSA staff will work to help you resolve it.
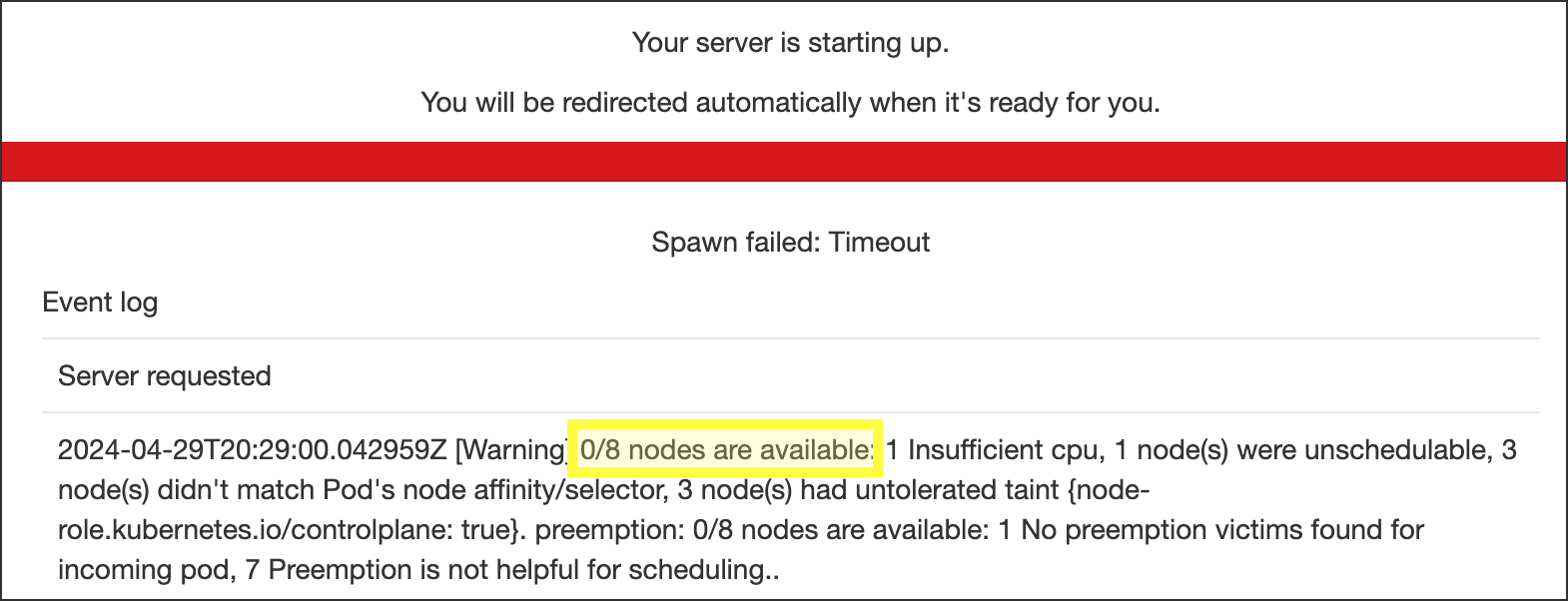
“0/<X> Nodes are Available” Error
As your server is starting, if you receive an error message that includes “0/<X> nodes are available”, the associated system node(s) have reached capacity. There are two options to resolve this:
Try again later. Once a node is below capacity, you will be able to start your server.
Try a different server. You may be able to start one of the other server options if the associated system node(s) have available capacity.
The system administrators monitor system utilization and advocate for increases in system capacity as utilization dictates. If you are consistently unable to log into the system due to node availability, please submit a support request.
Stop Your Server
If your code is acting in an unexpected way, the first troubleshooting step to try is to stop and re-start your server. Follow the How to Change Server Options steps to stop and start your server.
Access Built-in Help Tools
Python and R have built-in help commands that you can use to learn more about other commands. To access help, enter help() in a console or notebook and follow the prompts.
The Help menus in JupyterLab and RStudio also include useful references.
Reset Your ICRN Environment
To reset your ICRN environment to its initial state, start by removing your Conda environments (except base). If your ICRN environment is not sufficiently reset after you remove your Conda environments, submit a support request.
Remove a Conda Environment
Follow these steps to cleanly remove (delete) a Conda environment that you have created:
In a terminal, use
conda env listto see a list of your environments.For each environment that you want to remove (except base), run the following command. Replace
<env_name>with the name of the environment you are removing.Warning
When an environment is removed, it cannot be restored.
conda remove --all -n <env_name>
After removing the conda environments you no longer need, run the following command to clean up unused packages and caches.
conda clean --all
Jupyter-Specific
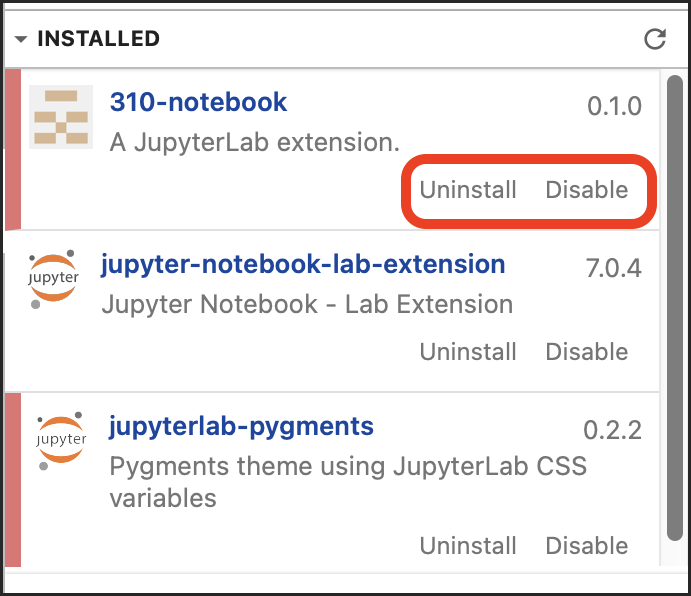
Uninstall a Recently Installed Extension
If you recently installed an extension (see Extensions) prior to experiencing issues with your code, uninstall the extension to see if that resolves the issue.
“The kernel for <>.ipynb appears to have died. It will restart automatically.”
If Python code in your notebook returns the error, “The kernel for <>.ipynb appears to have died. It will restart automatically.”, copy the code to a Terminal and run it there as a script.
Notebooks are limited to 8GB of memory. If your notebook uses more memory than that, this is the error message you will see. Running the code in a terminal will return more informative error messages to help you diagnose the issue and/or confirm it’s a memory usage issue.
RStudio-Specific
“Cannot remove…Device or resource busy”
If you get an error similar to the following when you try to remove (delete) a file in RStudio, the file is in use by R which is preventing it from being removed. To remove the file, change your image to a Jupyter instance and remove the file from Jupyter.
username@jupyter:~$ rm -rf file_name
rm: cannot remove 'file_name': Device or resource busy